Overview
Our simulation curriculum encompasses procedural training, including didactic and hands-on practical training for procedures such as:
- Central line placement (subclavian and internal jugular)
- Lumbar puncture (normal anatomy, obese patient, elderly patient with osteophytes)
- Thoracentesis
- Arthrocentesis
- Paracentesis
- Skin Biopsy
- Arterial line placement
- Intravenous catheter placement
- Pelvic Exam
Airway Management
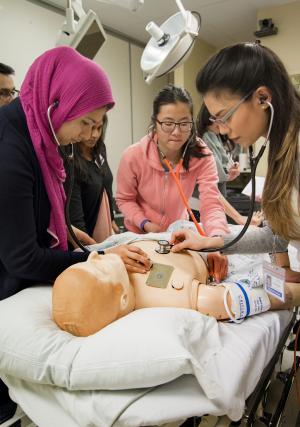 Additionally, airway management classes are held at regular intervals for training in endotracheal intubation (conventional and video-assisted), placement of laryngeal tubes and placement of laryngeal mask airways.
Additionally, airway management classes are held at regular intervals for training in endotracheal intubation (conventional and video-assisted), placement of laryngeal tubes and placement of laryngeal mask airways.
Airway classes are held in conjunction with the WWAMI Institute for Simulation in Healthcare (WISH) at the University of Washington and portions of the didactic training are provided via teleconferencing from Seattle.
Code Practice
The simulation curriculum also includes code practice, focusing on team organization, the “first four minutes," proper CPR technique, communication for code leaders, and Advanced Cardiac Life Support.
Scenario-Based Training
For scenario-based training, a combination of standardized patients and simulators are used. These scenarios include medical, surgical, and psychiatric conditions, and are often based on real patients that have been admitted and where additional practice is required.